INTRODUCTION
Masters Degree in Library and Information Science (MLIS) Programme comprises six core courses and two elective courses. In addition to theoretical, practical and seminar components of these courses (including electives), a student of MLIS Programme has to submit a Project/Dissertation (MLIP -002) which is considered as a 4 Credits full Course (100 marks). The purpose of Project/Dissertation is to provide an opportunity to the students to apply the knowledge they have acquired in course of their study and to develop skills in the areas of various courses of this Programme. IGNOU MLIP-002 Project Guideline
GENERAL GUIDELINES
Objectives
The general objectives of the Project/ Dissertation Work (MLIP-002) are to help the learner to:
• develop research skills;
• solve research problems through `scientific method’ of investigation;
• develop writing, presentation, communication and analytical skills;
• develop ability to. apply multi disciplinary concepts, tools and techniques; and
• solve problems of libraries information centres, knowledge centres and similar other
organisations.
Within this framework, MLIP-002 has the following specific objectives to enable a learner to:
• identify and formulate research problems;
• write a good research proposal;
• identify and use appropriate research methodology;
• conduct scientific investigation in a systematic way;
• collect and analyse data; and
• apply appropriate tools, techniques and methods and statistics to the field of library and information science.
Types of Project/Dissertation Work
The Project/Dissertation work may be of any one of the following types and preferably from the emerging areas of library and information science:
i) Design and development of information system/ user interface/ information service and its components (action research);
ii) Inter-institutional study aimed at inter-institutional comparison of information networks/ information systems/ information services/ information products/ practices;
iii) Comprehensive case study (covering single library/ information centre/ information network/ information system);
iv) Users’ survey, field study (empirical study);
v) Survey of literature in any discipline (bibliographic/ bibliometric study).
vi) Users’ Sensitisation
vii) Information literacy – methods, techniques, case studies.
PROPOSAL FORMULATION AND SUBMISSION
Proposal Formulation
Synopsis of the proposed project should be prepared in consultation with the supervisor. The synopsis should clearly state the objectives, methodology and other details of the proposed project/ study to be undertaken. It should have full detail of the rationale, sampling, instruments to be used, limitations if any, and future directions for further research. The project proposal should be submitted in A4 size paper typed in double space along with a consent letter of the Supervisor/Guide (Appendix-III) and the proforma (Appendix-II) for approval. A learner can select a supervisor of his/her own choice. The eligibility of a person to become Supervisor/Guide is given below.
Qualifications of Supervisor/Guide
The minimum qualifications of the supervisor are as follows:
a) Ph.D in Library and Information Science.
Or
b) Master’s Degree in Library and Information Science with two years experience in a library or information centre and in a lecturers’ grade or its equivalent.
Or
c) B.E./B.Tech. (Computer Science)/M.C.A. or equivalent with minimum of two years experience in a reputed library. Library, information centre and similar organisation.
A student may choose his/her supervisor according to his/her choice. The proposal should be accompanied by a bio-data of the supervisor, duly signed by him/her. The names of the external guides/supervisors will be approved by the Faculty of Library and Information Science before the study is undertaken. A Supervisor/Guide can supervise upto a maximum of 5 students.
The Supervisor/Guide will be paid a token remuneration of Rupees one hundred (Rs.100/-) only for each project. He/She can claim Project Guidance fee using a Proforma (Appendix V), after submission of the project/ dissertation of the student(s).
Project Proposal Submission and Approval
Students should send Project Proposal Proforma alongwith one copy of the synopsis and Bio-data of the Supervisor and a consent letter to the Programme Coordinator (MLIS), Faculty of Library and Information Science, School of Social Sciences, Academic Complex, Block-F, IGNOU, Maidan Garhi, New Delhi – 110068 for approval. Proposals incomplete in any respect will be rejected straight way. The project proposal should contain sections on background of the study, objective, methodology, expected outcome etc. of the study. If the study is to be conducted on some population, the size of the populations to be studied should be mentioned. Student is advised to retain a copy of the synopsis. Proposals not accompanying above papers will not be considered for approval. Please submit proposal before the last date of submission.
Communication of Approval
A written communication regarding approval/ non-approval of the project will be sent to the student as per schedule mentioned at Section 4.7 of this Project Guide.
Resubmission of Project Proposal
In case of non -approval of the proposal the comments/suggestions for reformulating the project will be communicated to the student. In such a case the revised project synopsis should be submitted with a fresh Project Proposal form (Appendix-II) along with a copy of the current Proposal form bearing the comments of the Programme Coordinator
PROJECT REPORT/IDISSERTATION WORK
Structure
The final report should be in the following format:
a) Certificate
b) Acknowledgements
c) Table of Contents
d) Preface
e) Introduction
f) Objectives of the Study
g) Methodology
h) Analysis and Findings
i) Conclusion
j) References and Bibliography
k) Index
l) Appendices, if any
Standard of Bibliographic References
All bibliographic references should be alphabetically listed, and given in the References and Bibliography section in the following format:
Books:
Foskett, A.C. (1996). The subject approach to information. 5`h ed. London: Library Association Publishing.
Ghosh, S.B. and Satpathi, J.N. (eds.) (1998). Subject indexing systems: concepts, methods and techniques.
Calcutta: Indian Association of Special Libraries and Information Centres.
Journal Article:
Neelameghan, A. (1990) SR Ranganathan’s impact on knowledge organisation tools. Information Studies, 6(2), 77-80.
Book Chapter:
Khan, A.W. (2005). Distance education for development. In: Garg, S. et. al. (Eds.) Open and distance
education in global environment: opportunities for collaboration. New Delhi: Viva Books.
Internet Resource:
Denton, William (2003). How to make ,faceted classification and put it on the web.
(accessed on 01/12/2005).
Conference Paper:
Arora, Jagdish (2005). Institutional repositories as a vehicle for open access publishing. Presented in ICDE International Conference on Open and Learning and Distance Education, November 19-23. New Delhi: Indira Gandhi National Open University.
Course Material:
Gopinath, M.A. (1999). Evaluation of information storage and retrieval (ISAR) systems. In: MLIS-03, Block
3, Unit 12 course materials. New Delhi: Indira Gandhi National Open University.
Thesis:
Broze, Stefne Lenzmeier (2003). The role of information in cancer patients ‘ involvement in their cancer care.
PhD Dissertation. Ohio: Ohio State University.
Physical Format
The length of the report may be about 80 to 120 double spaced typed pages not exceeding approximately 20,000 words (excluding appendices and exhibits). However 10% variation on either side is permissible. Report should be in A4 size papers and in a bound form. The language to be followed for the Project/Dissertation work should be in English.
Each project report must adequately explain the research methodology adopted. The project report should also contain the following:
a) Copy of Approved Project Proposal Proforma
b) Certificate of Originality duly signed by the student and the supervisor
Submission of Project Report/Dissertation
One copy of Project Report/ Dissertation is to be submitted to the Director (SR&E), IGNOU, Maidan Garhi, New Delhi – 110068. The Project Reports may be submitted either by insured registered post/insured speed post or by hand in SR&E Division, IGNOU, Maidan Garhi, New Delhi-110068.
“PROJECT REPORT – MLIS” should be written prominently on the top of the envelope. This will facilitate sorting of Project Reports for various programmes received in SR&E Division. The Project Report/Dissertation should be accompanied by a copy of the proforma (Appendix-II) in which the approval for the proposal has been given.
The Project Report/Dissertation may be submitted in either of the two slots, i.e., in April each year for accountability in June Term End Examinations, or in October each year for accountability in December Term End Examinations.
Evaluation of Project Report/Dissertation
The Project Report/ Dissertation will be evaluated by the Faculty or External Expert, as necessary. There
will be no viva-voce for evaluation of the project/ dissertation.
For successful completion of the projects, a student should secure a minimum of 50% marks in the
Project/Dissertation work.
Resubmission of Project Report/Dissertation
In case a student fails to qualify in Project/Dissertation Work, he/she can complete it within a stipulated time frame of the Programme, after incorporating suggestions made in earlier submitted report. However, he/she has to pay an additional amount for re-submission of the Project Work.
In case a student fails to clear the Project/Dissertation Work within the stipulated time frame, he/she may submit the Project Work within next 2 years with a payment of additional amount.
Exemption from Project Report/Dissertation Work
Project/Dissertation Work is an essential component of MLIS Programme and as such no candidate is exempted from completing this part for the award of the degree of MLIS.
You can check MEDSP-05 Project Guideline
Date of Submission
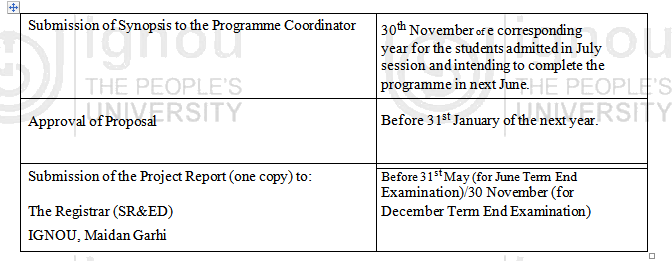
The schedule for submission of Proposal and Final Report for the academic session 2007-08 is as follows:
LIST OF PROBABLE AREAS FOR PROJECT/ DISSERTATION WORK
An illustrative list of topics is enclosed (Appendix I) to give you an idea as to what kind of topics could be selected for project work/dissertation work. A student may take up a topic related to a core course or an elective course of MLIS Programme. Student can select a topic, which may have substantial scope for innovation, or, which may originate new knowledge, or, which is from the emerging areas of information/ knowledge society.
POINTS TO REMEMBER


List of Areas for Project/Dissertation Work
A list of areas for which the Project/Dissertation Work may be carried out is given below. These are only illustrative and not exhaustive.
1. Study of the problems and constraints in initiating library automation in different organizations.
2. Library resources sharing.
3. Comparative study of library and information services of government-funded institutions and self-finance institutions.
4. Library consortia in corporate libraries.
5. Design of web-based information services for the visually challenged persons.
6. Development of Internet-based common gateway.
7. Study of campus wide information networks.
8. Impact of intellectual property rights on information services.
9. Study of professional skills requirements in the knowledge process outsourcing industry.
10. Study of metadata practices in digital repositories.
11. Development of special classification scheme on open and distance education.
12. Development of thesaurus on open and distance learning.
13. Study of marketing strategies in electronic information products.
14. Study of technical writing tools (software packages, style guides, etc.) used in the software industry.
15. Information seeking behaviour of different types of users.
16. Development of Internet-based learning management system for information professionals.
17. Bibliometric/scientometric/webometric studies.
18. Preservation and conservation of library materials.(Case Study of a )
19. Impact of electronic publishing in different types of libraries.
20. Comparative study of information infrastructure in India.
21. A comprehensive study of library associations in India.
22. Online repositories for scholarly materials.
23. Self-archiving of research publications.
24. Comparative study of special classification schemes in S&T disciplines
25. Impact of e -journals published by Indian researchers – a webometric analysis.
26. The usage patterns of online journals vs. printed journals.
27. Cost effectiveness in consortium based subscriptions models.
28. Analysis of central government budgets in development of library and information services in India.
29. Quality management of libraries and information centres.
30. Impact of ICT in the present society
31. Impact of ICT on library and information services.
32. Automatic indexing, web indexing etc.
33. State of the art reports on any emerging areas of Library and Information Science.
